Biodiversity Conservation and Ecosystem
Restoration in the Lake Chad Basin
Home
>
Biodiversity Conservation and Ecosystem Restoration in the Lake Chad Basin
Safeguarding Nature for Sustainable Development
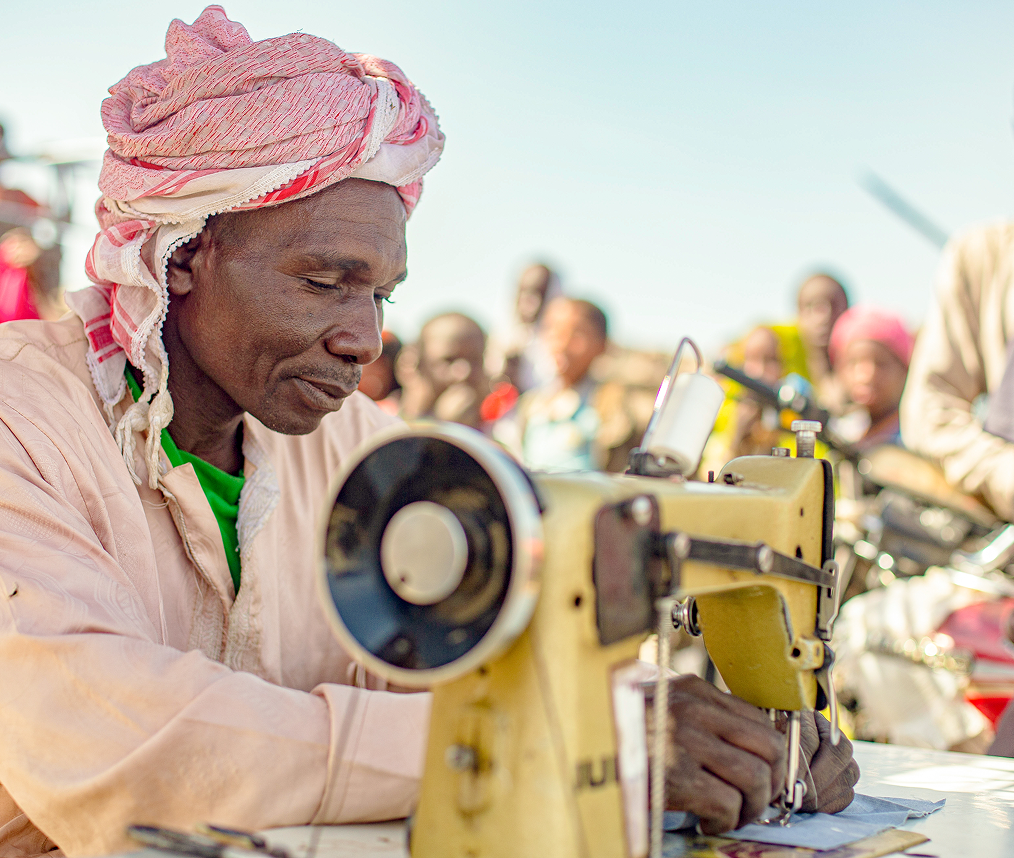
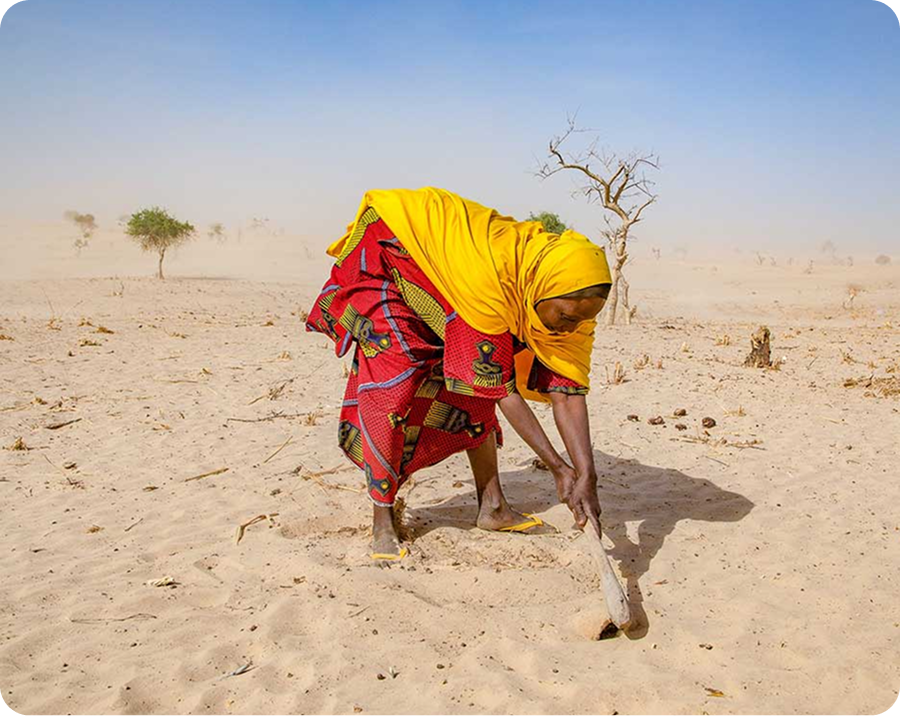
The Lake Chad Basin has a wealth of flora and fauna, particularly with various species of fish and birds. Protected areas of international importance were created to protect these species, but they are often poorly managed. The desert landscapes, shrub-steppes, savannah areas, forest, wetlands, and mountainous areas of the Basin make up the ecosystem. However, climate in the Lake Chad Basin is Sahelian, mostly characterized by a very short rainy season and a long dry season for the rest of the year. LCBC is working with various stakeholders to reverse the effects of climate change and biodiversity degradation.

Why Biodiversity Matters
Biodiversity is the foundation of life in the Lake Chad Basin. It ensures:

Food security
Through fisheries, agriculture
and livestock.

Water purification
And climate regulation via wet-lands and forests.

Livelihoods
For local communities through natural resource use.

Cultural heritage
And traditional knowledge embedded in nature.
Preserving biodiversity is essential for achieving the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), enhancing resilience, and promoting peace and stability in the region.
Looking Ahead
LCBC envisions a Lake Chad Basin where biodiversity thrives, ecosystems are resilient, and communities live in harmony with nature. Through the implementation of the RBAP, SAP, and other strategic instruments, LCBC is building a future where conservation and development go hand in hand.
Together with Member States, partners, and communities, LCBC is restoring the natural wealth of the Basin—ensuring that it remains a source of life, prosperity, and peace for generations to come.
Achievements and Innovations
Creation of Biosphere
Reserves
Enhancing transboundary
conservation.
Community-Based
Conservation Projects
Empowering local actors
Integration with Climate
& Disaster Strategies
Ensuring coherence.
Gender-Inclusive Approaches
Promoting equity in biodiversity
management.
Key Pillars of Biodiversity and Restoration

Protection of Endangered
Species and Habitats
· Annual inventories & ecological monitoring.
· Designation and management of protected areas and Ramsar sites.
· Conservation of endemic and threatened species.

Restoration of Degraded Eco-systems
· Reforestation and revegetation campaigns.
· Rehabilitation of wetlands, flood plains, and buffer zones.
· Control of invasive species and promotion of their economic use.

Sustainable Use and Community Engagement
· Promotion of income-generating activities linked to biodiversity.
· Support for agroecological practices and renewable energy.
Capacity building for indigenous peoples, women, and youth.

Knowledge, Monitoring, and
Governance
· Development of biodiversity databases and monitoring systems.
· Integration of biodiversity into national policies and development plans.
· Strengthening legal frameworks and stakeholder participation.
LCBC’s Strategic Approach
LCBC’s biodiversity and ecosystem restoration efforts are guided by:
· Regional Biodiversity Action Plan (RBAP 2023–2028): A roadmap for
restoring habitats, protecting species, and promoting sustainable use.
· Strategic Action Programme (SAP 2023–2037): Integrates biodiversity into
water governance, climate adaptation, and land restoration.
· Water Charter (2012): Embeds biodiversity protection in water resource
management.
· Climate Change Adaptation Strategy and DRR Framework: Aligns
biodiversity conservation with resilience-building.