Regional Strategy for the Stabilization, Recovery and Resilience of the Boko Haram affected Areas of the Lake Chad Basin Region
The four countries bordering Lake Chad, namely Cameroon, Chad, Niger, and Nigeria are facing unprecedented challenges intensified by repeated violence perpetrated by Boko Haram and other extremist groups. The resulting instability has slowed down economic growth and worsened existing environmental and developmental challenges in the Lake Chad Basin region.
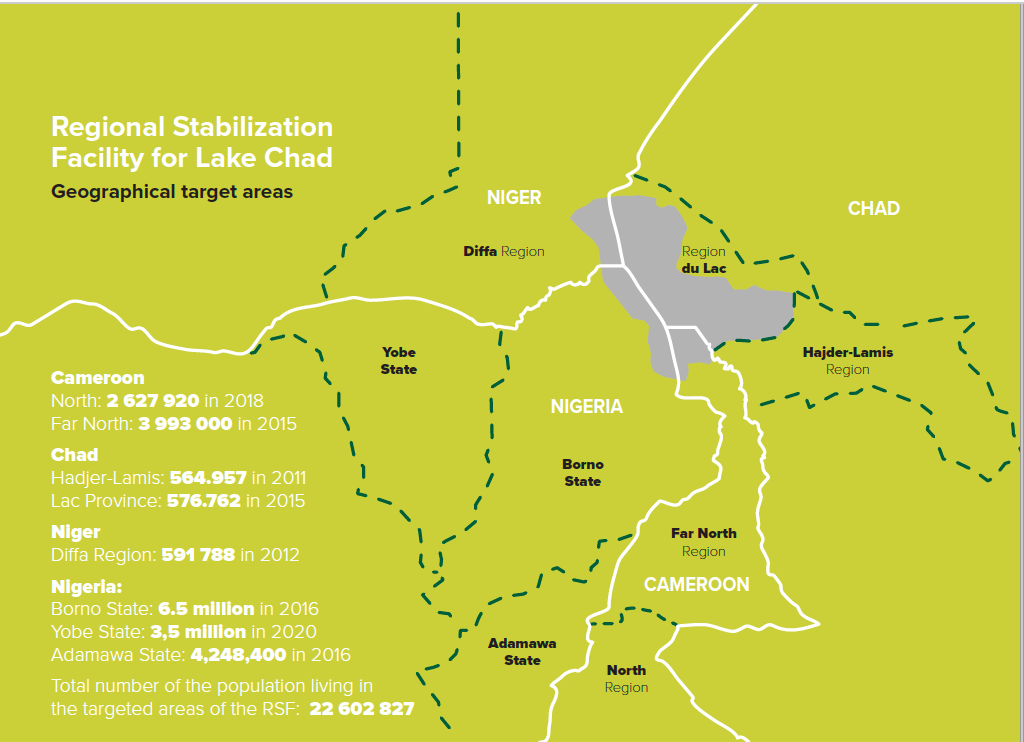
In a bid to ensure stabilization of the region, on 30 August 2018, the Council of Ministers of LCBC adopted the Regional Strategy for the Stabilization, Recovery and Resilience (RSS) of the Boko Haram-affected areas of the Lake Basin Region. The RSS was endorsed by the Peace and Security Council (PSC) of the African Union. The strategy develops an overarching regional approach in dealing with the deep-rooted causes of under-development and the drivers of violent extremism and conflicts in the Lake Chad region. It is being implemented in eight targeted territories of the four member states. They include:
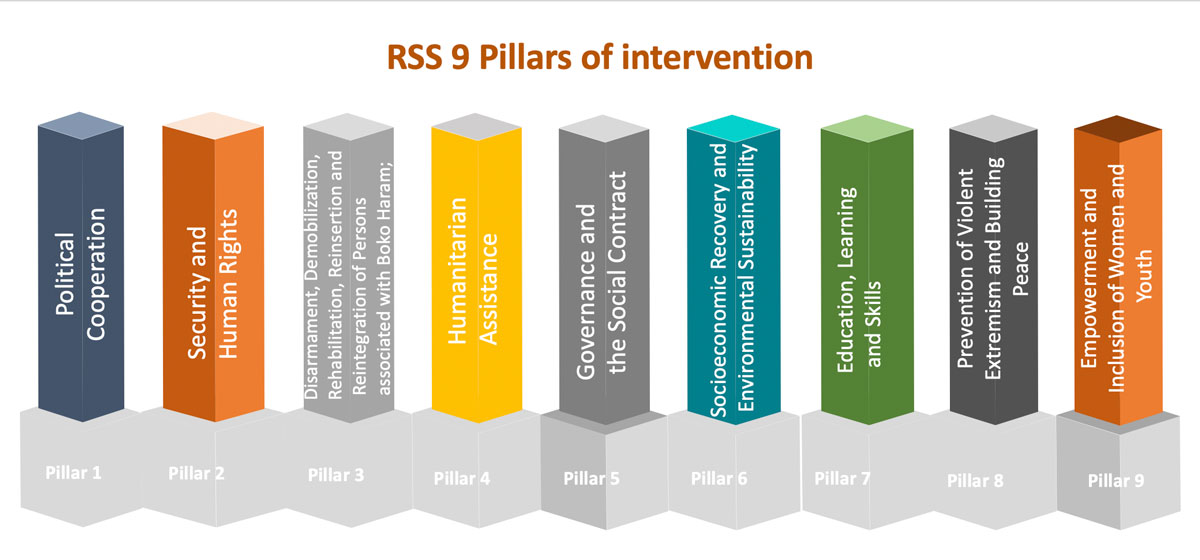
The RSS is structured around nine inter-related strategic pillars of intervention that define the broad scope of work to achieve its objectives. They include military support, provision of humanitarian assistance and key interventions to secure early recovery and longer-term resilience. The nine strategic pillars are:
The RSS is a product of broad consultations among experts of LCBC, African Union Commission, relevant agencies of the United Nations (UNDP) and other stakeholders. Its implementation is being led by LCBC, which is mandated to manage Lake Chad and other shared water resources in its basin, preserve the ecosystems of the Lake Chad Basin and promote regional integration, peace and security throughout the basin
